Imaginary Joints and Muscles
(SIGGRAPH 2025)
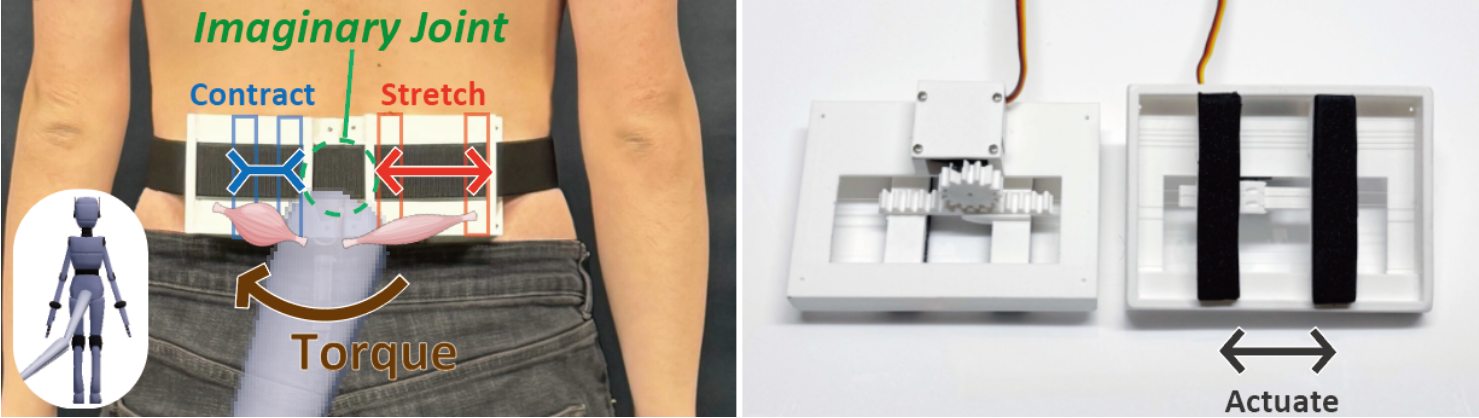
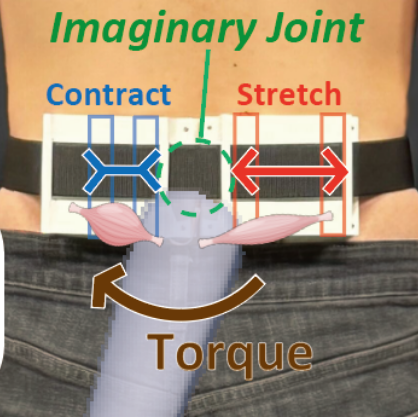
Extended body parts such as a third arm or tail have the potential to offer users new bodily experiences and capabilities. In this paper, we propose a method to enable users to intuitively perceive the posture and motion of such extended body parts without relying on vision, by introducing the concept of ”Imaginary Joints and Muscles”. Our approach provides proprioceptive feedback based on torque information via skin stretch. Specifically, we place an ”Imaginary Joint” at the interface between the user’s body and the extended body part, and the skin around the joint is stretched or compressed in accordance with the motion of the extended body. This allows the user to recognize the movement, in a modality close to innate proprioceptive sensation. The system calculates the torque required for the movement of the extended part and feeds it back to the user, making it applicable to a wide range of scenarios—including physics-based simulations, animations, externally induced movements and mapped manipulations. Through our demonstration, we show that multiple extended parts and various